新闻资讯/NEWS
|
|
Study diligently! Harvard University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology joint article: Empowering Biomedical Discovery with AI Agents!
The article proposes a vision of using AI agents as "scientists", combined with human creativity and professional knowledge, to analyze large datasets, explore hypothesis spaces, perform repetitive tasks, and accelerate the biomedical discovery process.
Introduction
The article first presents the long-term vision of AI in the biomedical field, which is to develop AI systems capable of making significant scientific discoveries and achieve the so-called "Nobel Turing Challenge.". The authors discussed the development of agent based AI, which can perform skeptical learning and inference by coordinating large language models (LLMs), machine learning (ML) tools, experimental platforms, or a combination of them.
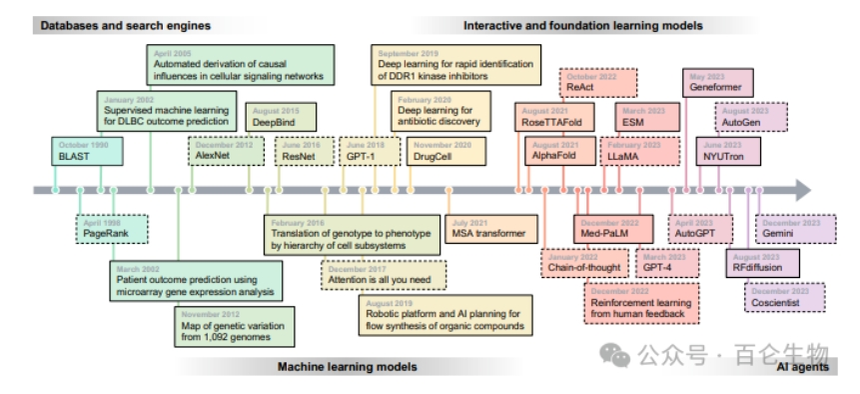
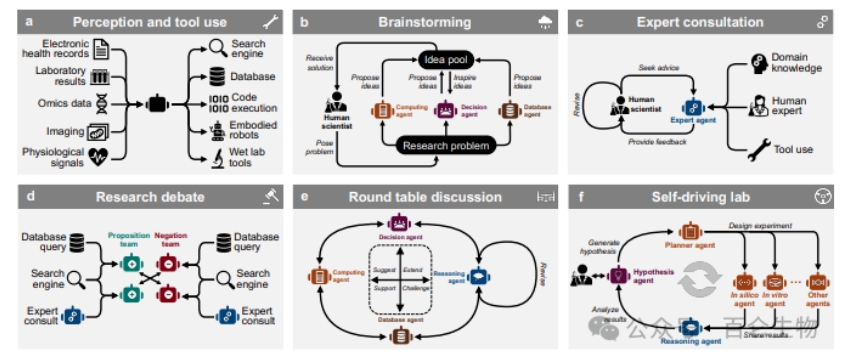
Figure 1: Utilizing AI agents to enhance biomedical research. AI agents have paved the way for "artificial intelligence scientists" who can engage in skeptical learning and reasoning. These multi-agent systems are composed of agents based on dialogue based large language models (LLMs) and can coordinate machine learning (ML) tools, experimental platforms, humans, or even their combinations. Specifically, it includes: Robot agent: an AI agent that operates robot hardware for physical experiments; Database proxy: an AI proxy that can retrieve information in the database through "function calls" and APIs; Inference agent: an AI agent that can perform direct reasoning and reasoning with feedback; Hypothesis agent: an AI agent with creativity and skepticism in developing hypotheses, capable of characterizing their own uncertainty and using it as a driving force to improve their scientific knowledge foundation; Brainstorming agents: AI agents that generate a wide range of research ideas; Search engine agent: an AI agent that uses search engines as tools to quickly collect information; Analysis agent: an AI agent that can analyze experimental results to summarize, discover, and synthesize concepts; Experimental Planning Agent: An AI agent that optimizes experimental plans for execution. 2. Evolution of data-driven models The article reviews how data-driven models have reshaped biomedical research over the past few decades through the development of databases, search engines, machine learning, and interactive learning models. These models advance the modeling of proteins, genes, phenotypes, clinical outcomes, and chemical compounds by mining biomedical data. Database and search engine: Aggregating experimental and research knowledge, providing searchable repositories containing standardized biological data vocabulary. Machine learning models perform well in recognizing patterns and integrating latent knowledge, and are able to make predictions on new data. Interactive learning model: improves the adaptability and efficiency of ML technology through exploration and feedback mechanisms.
3. Types of biomedical AI agents The authors distinguished between AI agents based on large-scale language models and multi-agent AI systems. LLM based agents can access tools and simulate the professional knowledge of human experts through pre training and domain fine-tuning. Multi agent systems combine agents with different capabilities, each with specialized tools and domain specific knowledge to improve task execution efficiency.
4. Autonomy level AI agents are divided into four levels of autonomy based on their abilities in hypothesis generation, experimental design, and inference. From Level 0 (without AI agents, using ML models as tools) to Level 3 (AI agents as scientists, able to develop and infer hypotheses beyond the scope of existing research), each level represents an increase in the independence of AI agents in scientific research. Level 0: No AI proxy, ML model as a tool. Level 1: AI agents act as research assistants to perform narrow tasks defined by scientists. Level 2: AI agents act as collaborators and collaborate with scientists to refine hypotheses. Level 3: As a scientist, AI agents are able to develop and infer hypotheses beyond the scope of existing research.
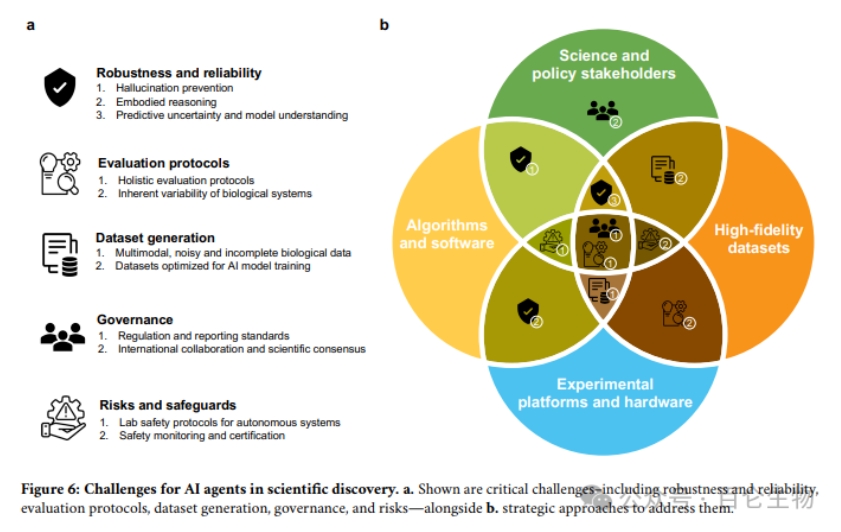
5. Building a roadmap for AI agents The article proposes the key modules required for building AI agents, including perception modules (enabling agents to understand and interact with elements in the environment), interaction modules (enabling agents to communicate with humans, other agents, and tools), memory modules (storing and retrieving knowledge), and inference modules (processing information and executing action plans). Perception module: enables agents to understand and interact with elements in the environment. Interaction module: enables agents to communicate with humans, other agents, and tools. Memory module: stores and retrieves knowledge, including long-term memory and short-term memory. Inference module: Process information and execute action plans. 6. Challenge Although AI agents have great potential in biomedical research, the authors also point out the challenges faced in implementing these agents, including technical barriers, evaluation protocols, dataset generation, governance, and risks and safeguards. Robustness and reliability: AI agents may generate unreliable predictions, including error messages and plan failures. Evaluation Protocol: An evaluation framework needs to be developed to evaluate the performance of AI agents. Dataset generation: A large, open, comprehensive, and easily accessible dataset is required to support model development. Governance: Establishing a governance framework to balance innovation and accountability. Risk protection measures: Ensure the secure deployment and use of AI agents.
7. Conclusion The article summarizes the potential of AI agents in biomedical research and emphasizes the importance of responsible development and deployment of these agents. The authors believe that by establishing trust, ensuring transparency, and continuous evaluation, AI agents can become powerful tools for accelerating scientific discovery and improving research efficiency.
|